Bluetooth is equated with the implementation specified by the Bluetooth Core Specification [3] group of standards maintained by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) industry consortium. The Bluetooth Toolbox functionalities enables you to model Bluetooth low energy (LE) and Bluetooth basic rate/enhanced data rate (BR/EDR) communications system links, as specified in the Core System Package [Low Energy Controller volume], Specification Volume 6. It also enables you to explore variations on implementations for future evolution of the standard. Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth LE devices operate in the same unlicensed 2.4 GHz Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) frequency band as Wi-Fi®.
In Bluetooth BR/EDR, the radio hops in a pseudo-random way on 79 designated Bluetooth channels. Each Bluetooth BR/EDR channel has a bandwidth of 1 MHz. Each frequency is located at (2402 + k) MHz, where k = 0,1,...78.
In Bluetooth LE, the operating radio frequency is in the range 2.4000 GHz to 2.4835 GHz, inclusive. The channel bandwidth is 2 MHz and the operating band is divided into 40 channels, k = 0, …, 39. The center frequency of the kth channel is located at 2402 + k × 2 MHz.
For more information about the specifications of Bluetooth BR/EDR and LE, see Comparison of Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth LE Specifications.
Bluetooth Connection Topologies
Most Bluetooth LE devices communicate with each other using a simple point-to-point (one-to-one communication) or point-to-multipoint (one-to-many communication) topology as shown in this figure.
Devices using one-to-one communication operate in a Bluetooth piconet. As shown in this figure, each piconet consists of a device in the role of Central, with other devices in the Peripheral or Advertiser roles. Before joining the piconet, each Peripheral node is in an advertiser role. Multiple piconets connect to each other, forming a Bluetooth scatternet....
继续阅读完整内容
请查看下方广告以解锁文章剩余内容
Bluetooth is equated with the implementation specified by the Bluetooth Core Specification [3] group of standards maintained by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) industry consortium. The Bluetooth Toolbox functionalities enables you to model Bluetooth low energy (LE) and Bluetooth basic rate/enhanced data rate (BR/EDR) communications system links, as specified in the Core System Package [Low Energy Controller volume], Specification Volume 6. It also enables you to explore variations on implementations for future evolution of the standard. Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth LE devices operate in the same unlicensed 2.4 GHz Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) frequency band as Wi-Fi®.
In Bluetooth BR/EDR, the radio hops in a pseudo-random way on 79 designated Bluetooth channels. Each Bluetooth BR/EDR channel has a bandwidth of 1 MHz. Each frequency is located at (2402 + k) MHz, where k = 0,1,...78.
In Bluetooth LE, the operating radio frequency is in the range 2.4000 GHz to 2.4835 GHz, inclusive. The channel bandwidth is 2 MHz and the operating band is divided into 40 channels, k = 0, …, 39. The center frequency of the kth channel is located at 2402 + k × 2 MHz.
For more information about the specifications of Bluetooth BR/EDR and LE, see Comparison of Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth LE Specifications.
Bluetooth Connection Topologies
Most Bluetooth LE devices communicate with each other using a simple point-to-point (one-to-one communication) or point-to-multipoint (one-to-many communication) topology as shown in this figure.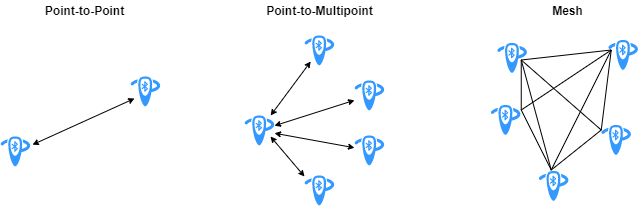
Devices using one-to-one communication operate in a Bluetooth piconet. As shown in this figure, each piconet consists of a device in the role of Central, with other devices in the Peripheral or Advertiser roles. Before joining the piconet, each Peripheral node is in an advertiser role. Multiple piconets connect to each other, forming a Bluetooth scatternet.
![]()
For example, a smartphone with an established one-to-one connection to a heart rate monitor over which it can transfer data is an example of point-to-point connection.
On the contrary, the Bluetooth mesh enables you to set up many-to-many communication links between Bluetooth devices. In a Bluetooth mesh, devices can relay data to remote devices that are not in the direct communication range of the source device. This enables a Bluetooth mesh network to extend its radio range and encompass a large geographical area containing a large number of devices. Another advantage of the Bluetooth mesh over point-to-point and point-to-multipoint topologies is the capability of self healing. The self-healing capability of the Bluetooth mesh implies that the network does not have any single point of failure. If a Bluetooth device disconnects from the mesh network, other devices can still send and receive messages from each other, which keeps the network functioning. For more information about Bluetooth mesh networking, see Bluetooth Mesh Networking.
Solution Areas
This table summarizes prominent solution areas of Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth LE.
| Application | Bluetooth BR/EDR | Bluetooth LE |
|
Audio streaming applications such as:
|
Supported | Supported |
|
Location and direction finding applications such as:
|
Not supported | Supported |
|
Data transmission applications such as:
|
Not supported | Supported |
|
Device network applications such as:
|
Not supported | Supported |
New Use Cases and Enhancements
These are some of the prominent new Bluetooth use cases and capabilities introduced by the SIG.
-
COVID-19 pandemic response solutions — To tackle the challenges of COVID-19 pandemic, many private and Government institutions have turned towards the Bluetooth technology for innovative solutions that can realize and accelerate reopening efforts across the world, and enable safer and faster treatment of patients during the COVID-19 pandemic and future disease outbreaks. To achieve these solutions, these three use cases leverage Bluetooth technology.
-
Exposure notification systems (ENS): Public ENS use the Bluetooth technology present in the smartphones to apprise people when they have been in close proximity with a person who was later diagnosed with COVID-19.
-
Safe return solutions: Public venues such as stadiums, offices, and universities etc. are looking to Bluetooth technology to provide safe return solutions to help them take necessary steps to reopen or continue to operate safely during the pandemic times. Some of the prominent solutions in these use case include occupancy management, exposure management, hygiene management, and touchless access and control.
-
Safe treatment solutions: Medical institutions are leveraging Bluetooth technology to improve the quality and efficiency of diagnosis and treatment. Some of these solutions include safe facility management, safe patient diagnosis and monitoring, remote patient care and monitoring.
-
-
Networked lighting control — Networked lighting control systems feature an intelligent network of individually addressable and sensor-rich luminaries and control elements that enable each device of the system to send and receive data. Bluetooth networked lighting control systems are deployed in offices, retail, healthcare, factories, and other commercial places to provide a combination of significant energy savings, improved occupant well-being and productivity, and efficient building operations and predictive maintenance. The key advantages of shifting from wired to wireless solutions for networked lighting control are reduced operation and maintenance cost, greater design and configuration flexibility, and future extensibility.
-
Bluetooth LE audio — The Bluetooth Core Specification 5.2 [2] introduced the next generation of Bluetooth audio called the LE audio. LE audio operates on the Bluetooth LE standard. LE audio is the next generation of Bluetooth audio, which supports development of the same audio products and use cases as the classic audio. It also enables creation of new products and use cases and presents additional features and capabilities to help improve the performance of classic audio products. Some of the key features and use cases of LE audio include enabling audio sharing, providing multistream audio, and supporting hearing aids. For more information about LE audio, see Bluetooth LE Audio.
References
[1] Bluetooth Technology Website. “Bluetooth Technology Website | The Official Website of Bluetooth Technology.” Accessed December 14, 2021.
[2] Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG). "Bluetooth Core Specification." Version 5.2.
[3] Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG). "Bluetooth Core Specification." Version 5.3.